
Electrical A 4 bit counter d flip flop with + 1 logic Verilog
Verilog D Flip-Flop Verilog Code Updated: December 15, 2023 No Comments 4 Mins Read Pinterest LinkedIn WhatsApp Email D Flip-Flop The output of a D Flip-Flop tracks the input, making transitions that match those of the input. The D in D Flip-Flop stands for Data, indicating that this Flip-Flop stores the value on the data line.

Tutorial 28 Verilog code of JK Flip Flop VLSI Verilog
What is D-Flip Flop? Implementation with Verilog. - YouTube Developers Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket © 2024 Google LLC Here, I have explained.

D FLIP FLOP VERILOG PROGRAM IN STRUCTURAL MODELING YouTube
A D flip-flop is a sequential element that follows the input pin d at the clock's given edge. D flip-flop is a fundamental component in digital logic circuits. There are two types of D Flip-Flops being implemented: Rising-Edge D Flip Flop and Falling-Edge D Flip Flop.

Design D Flip Flop using Behavioral Modelling in VERILOG HDL YouTube
1 Answer. Sorted by: 3. In your simulator, the initial value of the D flipflop is undefined, hence the behavior of your circuit is undefined. You can take one of two approaches: Add an initial assignment to the flipflop: initial q <= 0; Add a reset signal to the flipflop, and toggle it from your simulation. Your always block should then be:

D Flip Flop Design in Verilog Using Xilinx ISE YouTube
1. Implement D-FF In this step, we are going to implement a D-FF with asynchronous reset. As the block diagram in Fig. 1 shows, D flip-flops have three inputs: data input (D), clock input ( clk ), and asynchronous reset input ( rst, active high), and one output: data output (Q). module dff ( input D, input clk, input rst, output Q );

D Flip Flop Explained in Detail DCAClab Blog
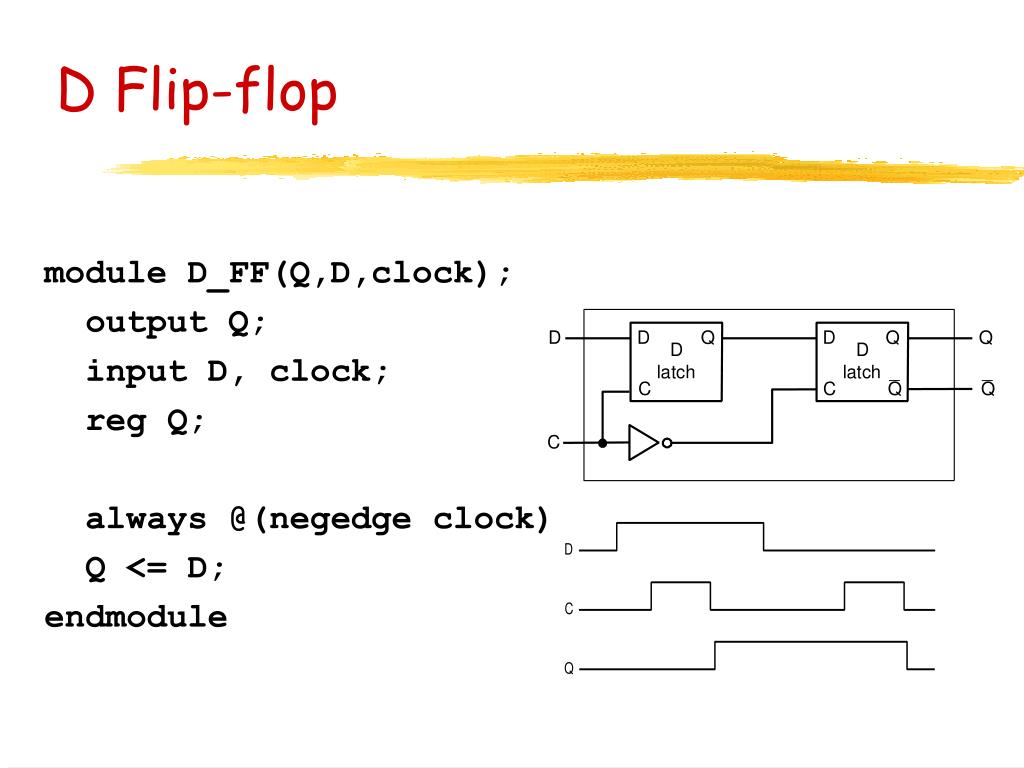
A D flip-flop stands for data or delay flip-flop. The outputs of this flip-flop are equal to the inputs. D flip flop Symbol As we proceed, we will see how we can design a D flip flop using different levels of abstraction Gate level modeling Gate level modeling uses primitive gates available in Verilog to build circuits.
DFF with synchronous reset
MaiaEDA FDRE: D flip-flop with clock Enable and synchronous Reset FDRE is a D-type flip-flop with an active-high clock enable (CE), and a synchronous active-high reset (R). R takes precedence over CE. The R and CE inputs are examined in priority order during the low-to-high transition of the clock (C) input. If R is asserted, Q is set to 0.
Solved Is this can be said 'Dflip flop used' verilog
Virtual Labs Design Of D-Flip Flop Using Verilog Verilog Verilog is language commonly used in designing digital systems. It is a hardware description language, which means that it is substantially different from any other language you might have encountered so far.

Design 8bit shift register (with Dflipflop)) using Verilog lab 13
7 This answer is not useful Save this answer. Show activity on this post. Does the statement q <= q; necessary? No it isn't, and in the case of an ASIC it may actually increase area and power consumption. I'm not sure how modern FPGAs handle this.
PPT Verilog II CPSC 321 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
In this video, we look at how to implement a positive edge triggered D Flip Flop in Verilog.

2 Verilog Description of D Flip Flop and Vivado Simulation YouTube
The Verilog code shown is an implementation of a D flip-flop module along with a testbench module to verify its functionality. The module is defined as d_flip_flop and has four input ports Q, D, clk, and reset.Q is the output port representing the current state of the flip-flop, D is the input port where the next state of the flip-flop is given, clk is the clock signal, and reset is the.

26 Describing D Latches and D FlipFlops in Verilog YouTube
D Flip Flops are used for storing a single bit of data. Here's an example of a D Flip Flop in Verilog and SystemVerilog: module DFF ( input logic D, clk, rst, output logic Q, Qn ); always_ff @ ( posedge clk, posedge rst) begin if (rst) begin Q <= 0 ; Qn <= 1 ; end else begin Q <= D; Qn <= ~D; end end endmodule

Verilog code for D flipflop All modeling styles
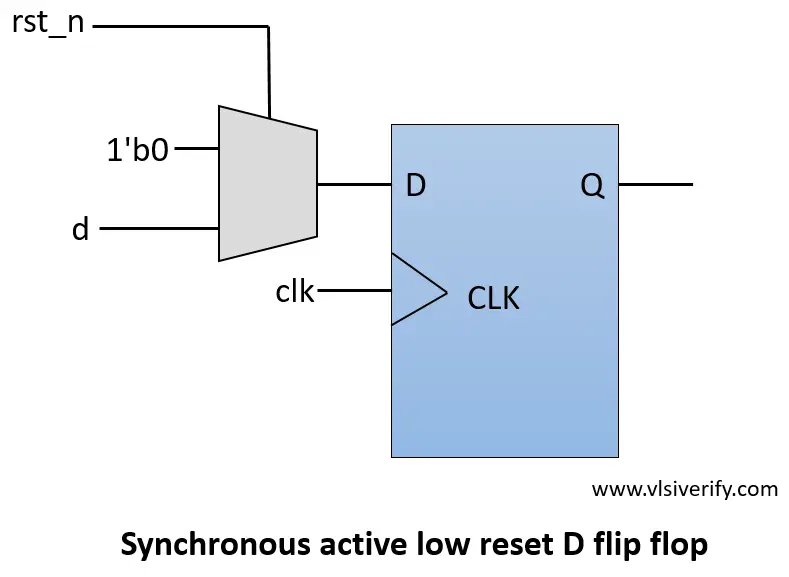
1.1 D Flip Flop with Synchronous Reset Verilog Code. 1.2 Testbench Code. 1.3 Waveform. D Flip Flop with Synchronous Reset. The below D flip flop is positive edge-triggered and synchronous active low reset D flip flop. As soon as reset is triggered, the output gets reset on the next posedge of a clock.

Verilog code for D flipflop All modeling styles
The basic working of D Flip Flop is as follows: When the clock signal is low, the flip flop holds its current state and ignores the D input. When the clock signal is high, the flip flop samples and stores D input. The value that was previously fed into the D input is reflected at the flip flop's Q output. If D = 0 then Q will be 0.
Verilog Test Bench Code For D Flip Flop amberandconnorshakespeare
Verilog Module Figure 3 shows the Verilog module of D Flip-Flop.The input to the module is a 1-bit input data line D.The control lines to the module include a 1-bit clock line Clk which is supplied by the 50 MHz on-board clock generator and a 1-bit active high reset.The output lines are Q and Qbar (complement of output line Q).The output line Q takes the same value as that in the input line D.
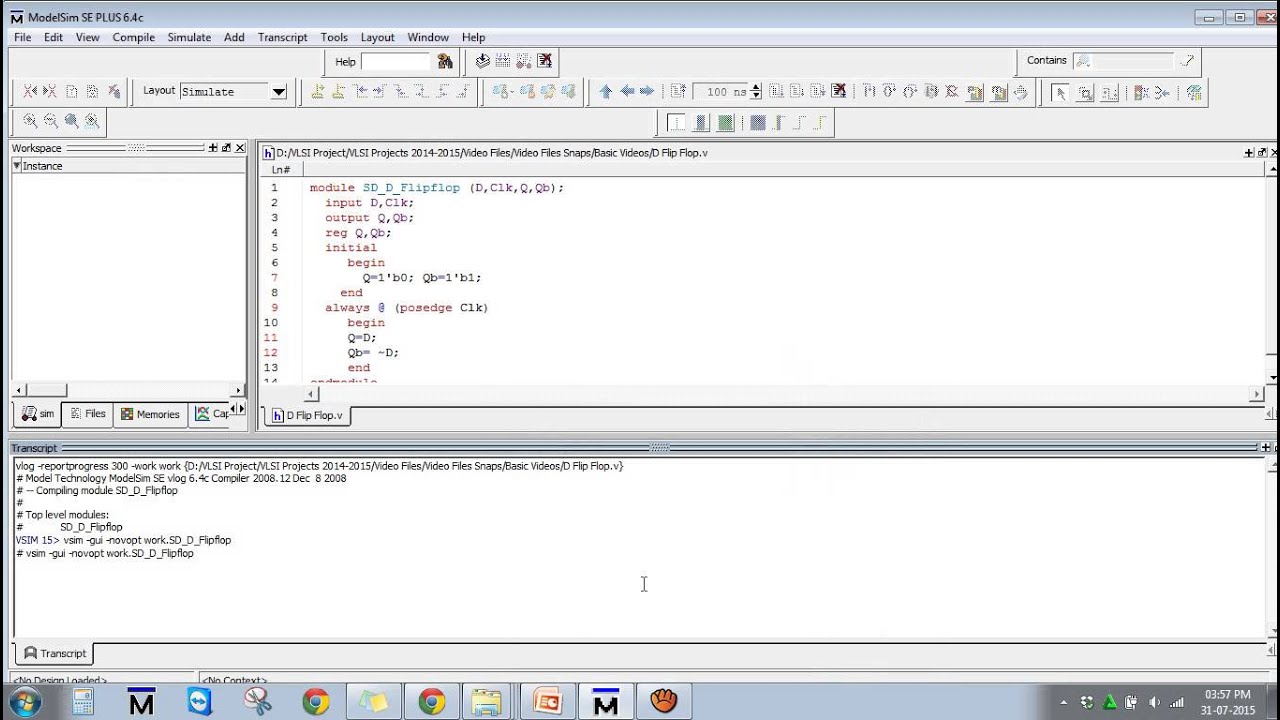
D Flip Flop Verilog Code and Simulation YouTube
D Flip-Flop is a fundamental component in digital logic circuits. Verilog code for D Flip Flop is presented in this project. There are two types of D Flip-Flops being implemented which are Rising-Edge D Flip Flop and Falling-Edge D Flip Flop. Verilog code for Rising Edge D Flip Flop: